Database Sharding vs. Partitioning: Understanding the Differences
In modern applications, databases are expected to handle millions or even billions of daily transactions. As data grows, so does the difficulty of efficiently storing, managing, and querying it. Two approaches often come up when scaling databases: partitioning and sharding.
Although these terms are sometimes used interchangeably, they are not the same. Both deal with splitting data, but their scope, purpose, and implementation differ significantly. Let's unpack concepts in detail.
What is Database Partitioning?
Partitioning is breaking a single database or table into smaller, more manageable pieces (partitions). All partitions exist within the same database system, but data is logically divided to improve query performance and manageability.
Think of it as organizing an extensive library into different sections: fiction, science, and history, while keeping all the books in the same building.
Types of Partitioning
-
Horizontal Partitioning: Splits rows based on a criterion (e.g., users by region, orders by month).
-
Vertical Partitioning: Splits columns into different tables (e.g., user profile info in one table, login credentials in another).
-
Range, List, or Hash Partitioning: Depending on how data is distributed (by values, ranges, or hash functions).
When to use partitioning:
-
When your dataset is large but can still fit on a single machine.
-
When queries often need to scan specific slices of data (e.g., time-based logs, financial records).
What is Database Sharding?
The sharding goes even further. Sharding removes data within one database to spread to several independent databases (shards), each executing on an independent server or cluster.
Each shard will be an autonomous database containing only part of the data. The query is decided on by the application (or middleware layer) depending on some shard key (such as user ID or geographic location).
Consider sharding as the opening of many branches of libraries in the city. The branches carry only some books, and visitors are sent to the appropriate branch depending on their requirements.
When to use sharding:
-
When your data volume or traffic is too large for a single database server to handle.
-
When scaling horizontally (adding more servers) is cheaper and more practical than vertically scaling one giant machine.
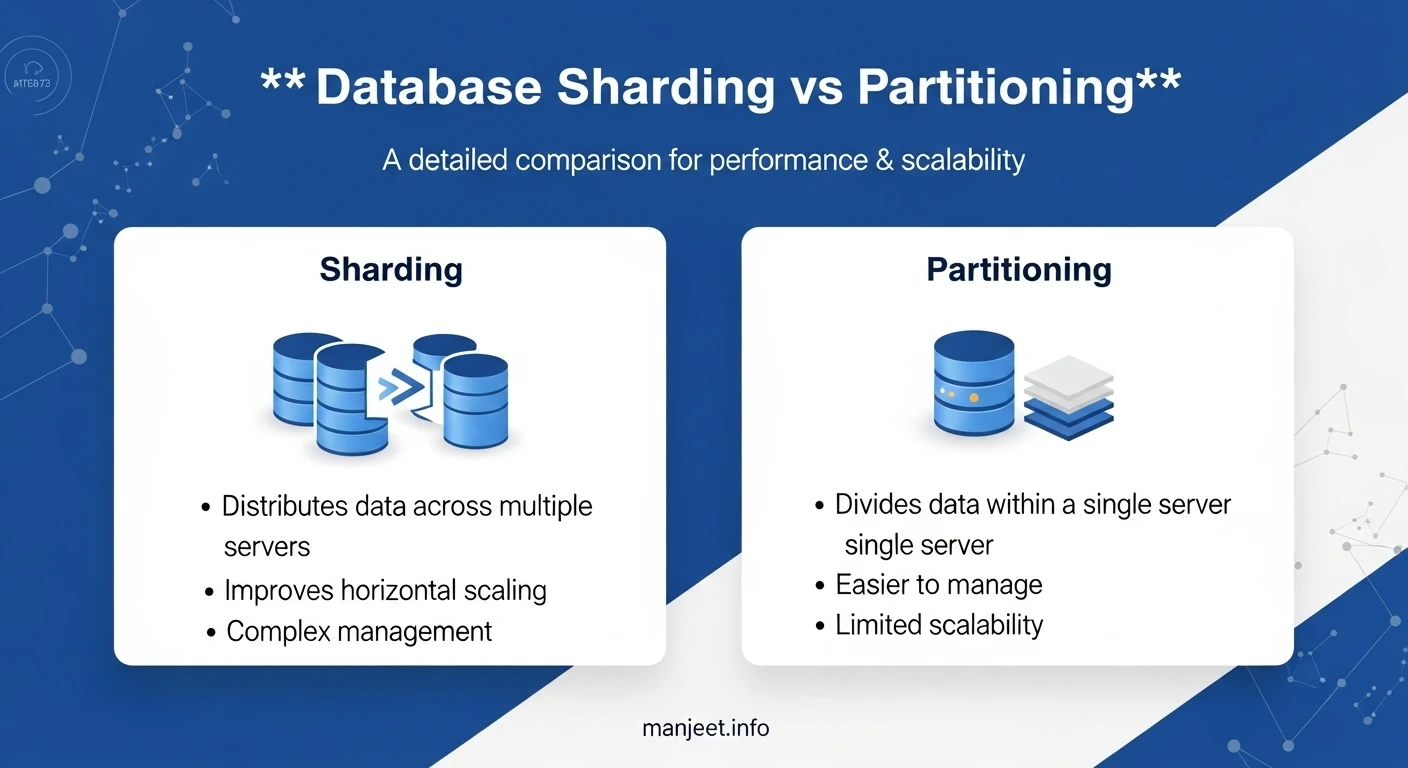
Partitioning vs. Sharding: Key Differences
| Aspect | Partitioning | Sharding |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Splits data inside a single database | Splits data across multiple databases/servers |
| Goal | Improve query performance and manageability | Achieve horizontal scalability |
| Complexity | Easier to implement, often supported by DB engines | More complex, requires routing logic or middleware |
| Scaling | Limited to one machine's camera | beyond a single machine |
| Use Case | Large tables, reporting, time-series data | High-traffic apps, global user bases, distributed systems |
Real-World Examples
-
Partitioning: Transaction records of billions of transactions are stored in a financial institution. It separates them year by year rather than storing them in one huge table. The 2023 transactions queries will only scan the partition in question and enhance performance.
-
Sharding: Hundreds of millions of users of a social media platform cannot be run in one database. It disperses users among servers. Users 1-10 million will access Shard A, 10-20 million will access Shard B, etc. In so doing, the load distribution will be distributed among machines.
Can You Combine Them?
Yes. Organizations use the two on a significant scale. Indicatively, a large e-commerce company can distribute users to several servers and subdivide each server internally using the order date. This stratified approach maintains high levels of performance but is scaled.
Final Thoughts
While both partitioning and sharding are about breaking data into pieces, they solve different problems:
-
Partitioning is about optimizing within a database.
-
Sharding is about scaling across databases.
The decision of partitioning versus sharding is primarily based on the size of the system and the expected growth of the system. The mid-sized systems typically require partitioning. Nonetheless, sharding is necessary for large-scale internet applications like Instagram, Amazon, or Uber to ensure scalability and performance.
Read also Scaling MongoDB for Billions of Documents: Best Practices for Data Storage and Processing